Informatics2-2021/Lab13
A MathWikiből
(Változatok közti eltérés)
(→Homework 9) |
(→Homework 9) |
||
| 18. sor: | 18. sor: | ||
==Numeric integral== | ==Numeric integral== | ||
Estimate the integral of <math>e^{-x^2}</math> on the interval <math>[-2,5]</math> with the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Riemann_sum#Left_Riemann_sum left Riemann sum]! | Estimate the integral of <math>e^{-x^2}</math> on the interval <math>[-2,5]</math> with the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Riemann_sum#Left_Riemann_sum left Riemann sum]! | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Numeric derivative== | == Numeric derivative== | ||
Plot the function <math>\sin(x)</math> and its derivative on the interval <math>[-\pi, \pi]</math>. | Plot the function <math>\sin(x)</math> and its derivative on the interval <math>[-\pi, \pi]</math>. | ||
Calculate the derivative with [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Finite_difference finite difference] method! | Calculate the derivative with [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Finite_difference finite difference] method! | ||
A lap 2021. május 11., 12:24-kori változata
Tartalomjegyzék |
Exercises
Introduction
Some exercises to get used to numpy
- Make a vector of length 10 with elements all zero! Then modify its 4th element to 1 (zeros)
- Make a 3-by-3 matrix with elements ranging from 0 up to 8 (reshape)
- Make a random vector of length 30 containing random number between 0 to 1! Calculate its average and standard deviation! (rand, mean, std)
- Make a random vector of the same length with elements between -3 and 2!
- Make a random unit vector in 5 dimensions! First make a random vector in 5 dimensions and then normalize it to unit length!
Monte-Carlo
Generate 500000 random points in the rectangle ![[0,2]\times[0,4]](/upload/math/d/1/f/d1f4d6baafac79655f4052ed2930bf35.png) . Count how many of the points (x,y) have the property that x2 > y. Use this to approximate the integral
. Count how many of the points (x,y) have the property that x2 > y. Use this to approximate the integral 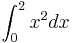 Like in the end of the lecture.
Like in the end of the lecture.
Homework 9
Each problem counts for 2 points
Numeric integral
Estimate the integral of 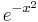 on the interval [ − 2,5] with the left Riemann sum!
on the interval [ − 2,5] with the left Riemann sum!
Numeric derivative
Plot the function sin(x) and its derivative on the interval [ − π,π]. Calculate the derivative with finite difference method!