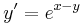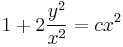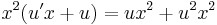Szerkesztő:Mozo/A3 gyakorló feladatok 5.
A MathWikiből
(Változatok közti eltérés)
Mozo (vitalap | szerkesztései) (→Fokszámban homogén egyenletek) |
Mozo (vitalap | szerkesztései) (→Fokszámban homogén egyenletek) |
||
| 47. sor: | 47. sor: | ||
:<math>u'x=u+u^2\,</math> | :<math>u'x=u+u^2\,</math> | ||
:<math>\int\frac{\mathrm{d}u}{u(u+1)}=\int \frac{1}{x}\mathrm{d}x\,</math> | :<math>\int\frac{\mathrm{d}u}{u(u+1)}=\int \frac{1}{x}\mathrm{d}x\,</math> | ||
| − | :<math>\int\frac{1}{u}-\frac{u+1}\mathrm{d}u=\int \frac{1}{x}\mathrm{d}x\,</math> | + | :<math>\int\frac{1}{u}-\frac{1}{u+1}\mathrm{d}u=\int \frac{1}{x}\mathrm{d}x\,</math> |
:<math>\ln|u|-\ln|u+1|=\ln |x|+C\,</math>; <math>(C\in\mathbf{R})</math> | :<math>\ln|u|-\ln|u+1|=\ln |x|+C\,</math>; <math>(C\in\mathbf{R})</math> | ||
:<math>\ln\left|\frac{u}{u+1}\right|=\ln c_1|x|\,</math>; <math>(c_1=\ln C\,)</math> | :<math>\ln\left|\frac{u}{u+1}\right|=\ln c_1|x|\,</math>; <math>(c_1=\ln C\,)</math> | ||
| 55. sor: | 55. sor: | ||
Explicit mo.: | Explicit mo.: | ||
:<math>y=\frac{cx^2}{1+cx}\,</math>; <math>(c\in\mathbf{R})</math> | :<math>y=\frac{cx^2}{1+cx}\,</math>; <math>(c\in\mathbf{R})</math> | ||
| + | ===Kezdetiérték feladat=== | ||
| + | '''1.''' <math>y'=e^{x-y}\,</math> | ||
A lap 2016. június 3., 22:12-kori változata
Differenciálegyenletek
Fokszámban homogén egyenletek
1. 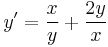
MO. u = y / x; y = ux; y' = u'x + u
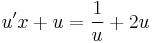
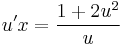

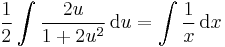
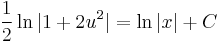 ;
; 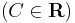
 ;
; 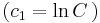
 ;
; 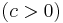
Implicit mo.:
Explicit mo.:

- Itt
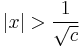
2. 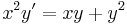
MO. y≡0 konstans mo. y=ux helyettesítéssel:
ahonnan intervallumon értelmezett megoldás esetén:
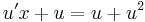
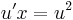
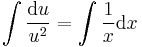
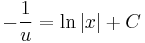 ;
; 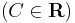
Implicit mo.:
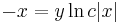 ;
; 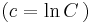 és y=0
és y=0
Explicit mo.:
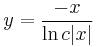 és y=0.
és y=0.
3. 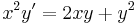
MO. y≡0 konstans mo. y=ux helyettesítéssel:
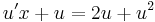
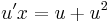
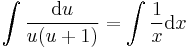
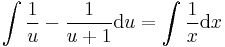
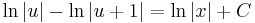 ;
; 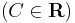
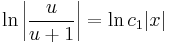 ;
; 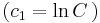
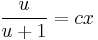 ;
; 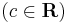
Implicit mo.:
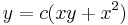 ;
; 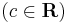
Explicit mo.:
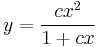 ;
; 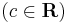
Kezdetiérték feladat
1.